Elasticsearch is a Java-based open-source distributed search engine built on Apache Lucene.
Through Elasticsearch, you can use the Lucene library (an information retrieval library developed in Java) independently, and perform near real-time storage, search, and analysis of massive amounts of data.
Elasticsearch can be used standalone for search purposes, or as part of the ELK (Elasticsearch / Logstash / Kibana) stack.
ELK Stack Components#
- Elasticsearch: Searches and aggregates data received from Logstash to obtain necessary information
- Logstash: Collects, aggregates, and parses logs or transaction data from various sources (DB, CSV files, etc.) and delivers them to Elasticsearch
- Kibana: Visualizes and monitors data through Elasticsearch’s fast search capabilities
💡 The ELK stack is primarily used to collect scattered logs from load-balanced WAS into one place, quickly search for desired data, and visualize it for monitoring purposes.
Elasticsearch and RDB Terminology Comparison#
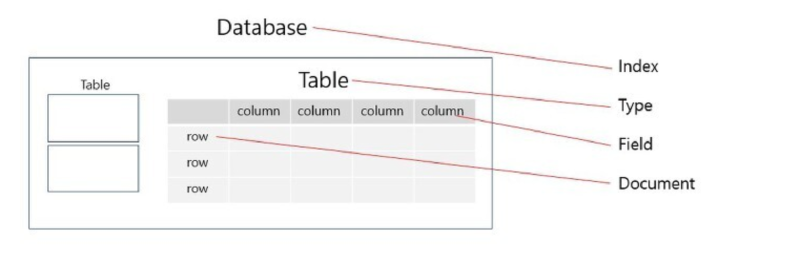
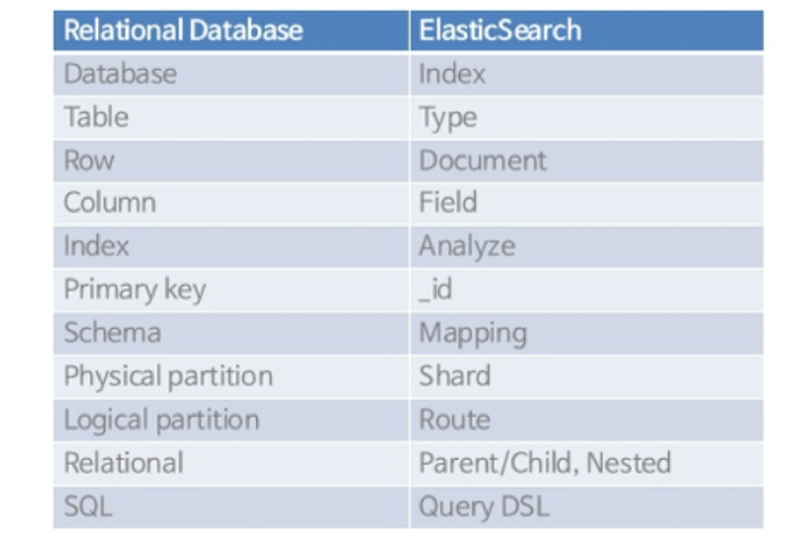
Elasticsearch 7.0+ Allows Only One Type Per Index#
The reason is that Elasticsearch uses the same Lucene fields for types within a single index (DB). Therefore, even if types are different, fields with the same name are not independent, which can cause various problems. As a result, it was modified so that one index can only have one type.
Comparison with RDB#
In the case of RDB
- A single DB can have multiple tables, and columns with the same name in each table do not affect each other.
In the case of Elasticsearch
- If there are fields (=columns) with the same name in each type (=table) within one index (=DB), those fields are not independent and are stored in the same Lucene field, requiring the same definition.
Elasticsearch Architecture#
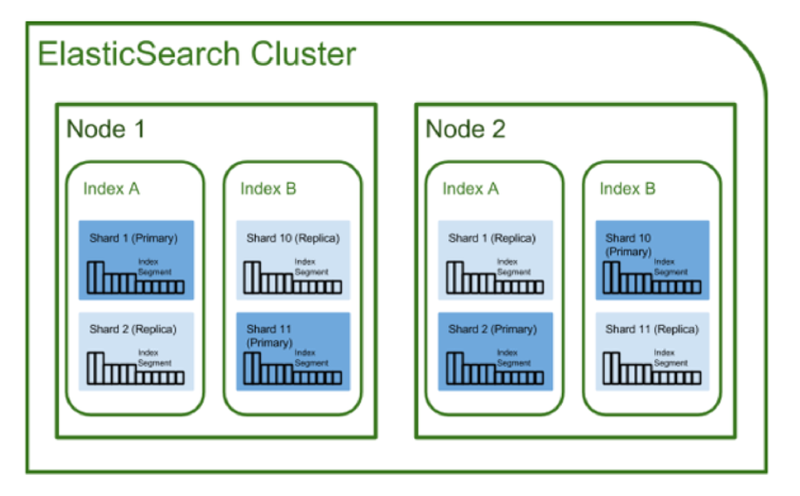
Cluster#
A cluster is the largest system unit in Elasticsearch, consisting of a collection of nodes with at least one or more nodes.
- Different clusters are maintained as independent systems that cannot access or exchange data
- Multiple servers can form a single cluster
- Multiple clusters can exist on a single server
Node#
A node is a single server included in a cluster that stores data and participates in the cluster’s indexing and search capabilities. Nodes are classified according to their roles as follows:
Master-eligible Node#
A node that can be selected as a master to control the cluster
- Creating and deleting indices
- Tracking and managing cluster nodes
- Selecting shards to allocate when data is input
Data Node#
A node where data (Documents) is stored and where shards, the spaces for distributed data storage, are placed
- Performs data operations such as CRUD, indexing, searching, and statistics
- Requires significant resources (CPU, memory, etc.)
- Requires monitoring and should be separated from master nodes
Ingest Node#
Executes pre-processing pipelines such as data transformation
Coordination Only Node#
A node that receives user requests and distributes them in a round-robin manner
- Forwards cluster-related requests to the master node
- Forwards data-related requests to data nodes
- Performs load balancing role
Index / Shard / Replication#
Index#
A concept corresponding to a database in RDB
Shard#
Data indexed within an index does not exist as a single unit but is divided into multiple parts. A single index is split into multiple shards for scale-out purposes.
💡 Shards are divided into primary shards and replica shards.
Primary Shard
- The original data
- Data update requests are sent to the primary shard
- Updated content is replicated to replica shards
Replica Shard
- A copy of the primary shard
- Used as a replacement when the original data is lost, performing a role in overcoming failures
- By default, assigned to a different node than the primary shard
Segment#
A segment is a data structure designed for fast document search in Elasticsearch and is a physical file containing shard data.
Segment Characteristics#
- Each shard consists of multiple segments, enabling efficient search through distributed processing of search requests
- When searching a shard, each segment is searched first, results are combined, and the final result is returned as the shard’s result
- Data indexed within segments is stored in an inverted index structure, making search speed very fast
Segment Creation Process#
Creating a new segment for every request would generate too many segments, so an in-memory buffer is used to prevent this.
Flush: When the content accumulated in the in-memory buffer reaches a certain time or the buffer is full, flush is performed and segments are created in the system cache
- Data becomes searchable from this point
- In this state, the segment is stored in the system cache, not on disk
Commit: After a certain time, segments are stored on physical disk through commit
Merge: Stored segments are merged into one over time
- By merging segments into one, the number of segments to search decreases, improving search performance


